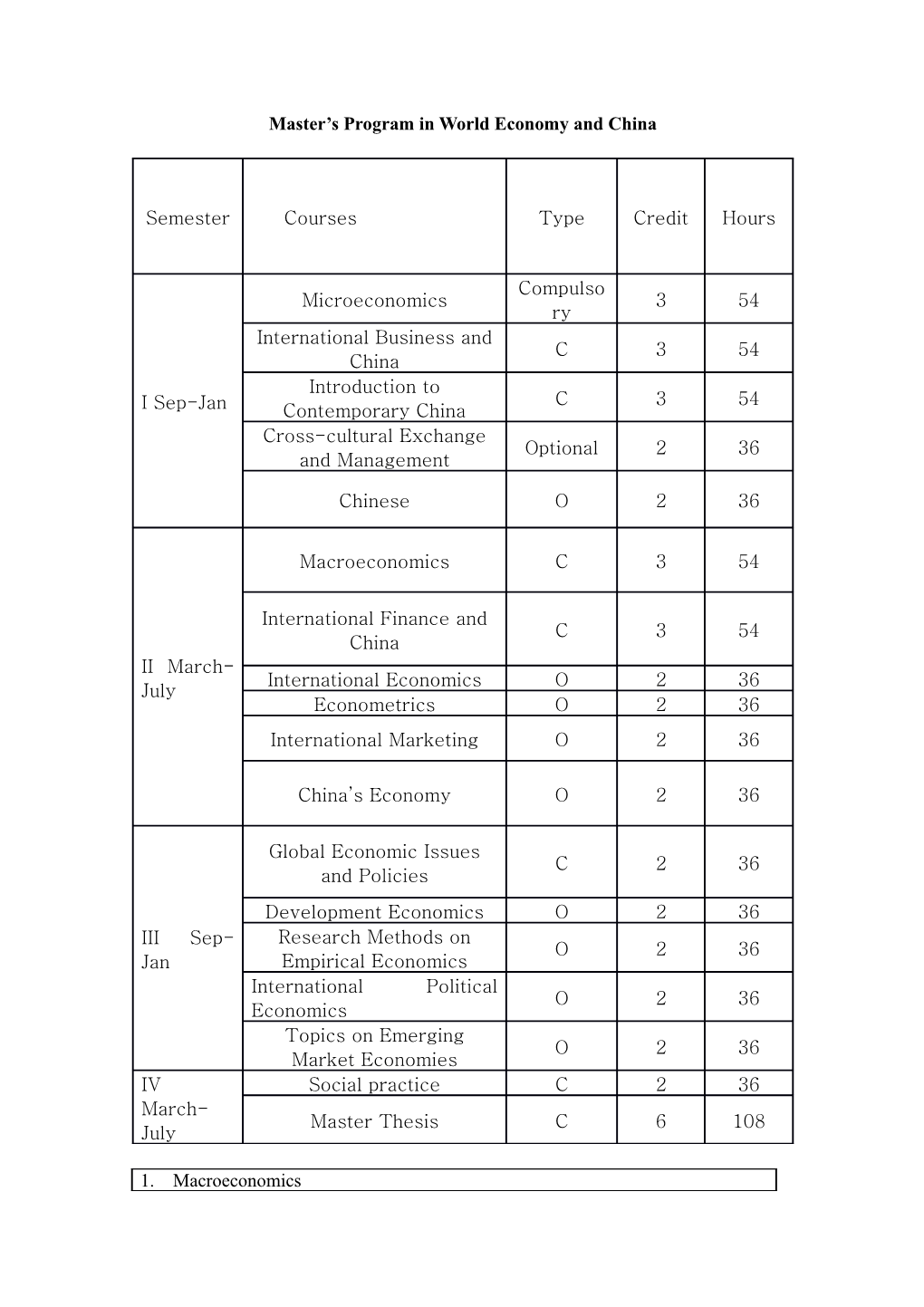
Master’s Program in World Economy and China
Semester / Courses / Type / Credit / Hours
I Sep-Jan / Microeconomics / Compulsory / 3 / 54
International Business and China / C / 3 / 54
Introduction to Contemporary China / C / 3 / 54
Cross-cultural Exchange and Management / Optional / 2 / 36
Chinese / O / 2 / 36
II March-July / Macroeconomics / C / 3 / 54
International Finance and China / C / 3 / 54
International Economics / O / 2 / 36
Econometrics / O / 2 / 36
International Marketing / O / 2 / 36
China’s Economy / O / 2 / 36
III Sep-Jan / Global Economic Issues and Policies / C / 2 / 36
Development Economics / O / 2 / 36
Research Methods on Empirical Economics / O / 2 / 36
International Political Economics / O / 2 / 36
Topics on Emerging Market Economies / O / 2 / 36
IV March-July / Social practice / C / 2 / 36
Master Thesis / C / 6 / 108
- Macroeconomics
This is a graduate level macroeconomic theory course. It is based on general equilibrium theory and aimed to develop skills and knowledge in advanced theoretical and empirical topics and methods necessary for high-level macroeconomic and policy analysis. The goal of this course is to provide graduate students with the necessary tools and techniques required to understand advanced macroeconomic modelling.After the course students will be able to apply these techniques to interesting issues in economic growth and development, public finance, money, labor, or other areas.
- Microeconomics
As an introduction to formal micro economic analysis of human and firm behavior and interaction, this course helps students to gain the ability to apply the microeconomic concepts covered in this class to formally solve economic problems.
- International Business and China
This course is an introduction to international business with an emphasis on the contemporary international trade issues of China. It will cover the main theories in international trade, their empirical relevance, and their role for Chinese economy. It will link these conceptual tools provided by international economics to the actual strategic and operational decisions of exporters and multinational enterprises. All topics will be presented through both theoretical and empirical papers including: What determines the pattern of international business? How does international business affect firm and the economy in terms of growth, income disparity, the environment etc.? What barriers impede the free flow of goods between countries? Do trade agreements actually create more trade? What comparative advantage does China have? How do firms decide to invest abroad? In particular, there are recent developments at the intersection of the theory of international trade and the theory of the firm for the analysis of the multinational and multiproduct firms' behavior.
- Introduction to Contemporary China
The course aims to provide students with an objective, impartial, analytical and up-to-date account of the problems faced and progress made by China in its interaction with the world economy. China’s transformation into a dynamic private-sector-led economy and its integration into theglobal economy have been among the most dramaticeconomic developments of recent decades. Indeed, China’s growth performance over the last twodecades has been spectacular, with GDP growth averaging almost 8 percent. China now ranks as thesixth largest economy in the world (at market exchange rates).
- Cross-cultural Exchange and Management
The purpose of this course is to offer tools for a lifetime of continued growth in intercultural competence, both on the professional and personal level as well as to develop awareness and increased understanding among people of different cultures. Using a variety of case studies, multimedia resources and group work, students will develop a personal and theoretical understanding of the cultural origin of people’s values, ideologies, habits, idiosyncrasies and how they affect communication across cultural, racial, ethnic and gender lines. Through observing, simulating and experiencing incidents of cross-cultural communication, they will begin to examine and develop skills that are necessary for effective understanding and for successful intercultural communication in business and private settings.
- Chinese
This is a Chinese conversation lessons, the lesson once a week. We mainly learn spoken Chinese. Group activity will be more used in class. Through the study of this course, students can use the Chinese language fluently in daily life.
- International Finance and China
To equip the students with knowledge on current international financial system, in macro and micro perspectives
To equip the students with a clear understanding on and basic ability of analyzing how balance of payments and exchange rate interplay for individual economies.
To equip the students with up-dated knowledge on China’s economy and external economic and financial relations.
- International Economics
Pure or "real" aspects of international trade, including the basic comparative advantage model, commercial policy (tariffs, quotas, etc.), economic integration, and the role of international trade in economic development. Monetary aspects of international trade, including international capital movements, foreign exchange market, concept and measurement of balance of payments, alternative means of correcting disequilibrium in the balance of payments, and international monetary arrangements.
- Econometrics
The goal of this course is to familiarize the student with the theory and practice of econometrics. Specifically, we want to learn how to interpret and use empirical results. Because econometric modeling is widely used in the analysis of policy and policy changes, decision makers and analysts must understand what econometric results are telling them and, just as importantly, what they are not telling.
- International Marketing
This course examines the impact of economic, cultural, political, legal and other environmental influences on international marketing. The students will learn how to identify and analyze worldwide marketing opportunities, and examine product, pricing, distribution and promotion strategies. Insights will be provided into the conceptual framework for marketing across national borders, as well as marketing within different foreign environments. The students will study how to evaluate the market potential of a targeted buyer/consumer segment, understand host culture requirements in relation to international marketing and choose appropriate tools for strategy implementation. Furthermore, different negotiation styles, distribution and logistical structures and well as pricing issues shall be given consideration. The course is structured to provide ample opportunity for interaction among students, and between students and the instructor.
- China's Economy
This course will summarize successful experience and lessons of failing with economic development and reform in China and put forward a general theory of economic development and transition. Based on this theory, the students can analyze the achievements, major economic and social problems in the China's economic development. In addition, we will also investigate the reasons and find out the solutions.
- Global Economic Issues and Policies
This course introduces the interdependent nature of the global economy, its current economic problems and the different policy perspectives and their impact. The goal of the course is for the students to be able to understand global economic concepts and theories and to apply them to policy analysis. Various global economic issues like protectionism, globalization, trade deficit, and exchange rate will be discussed.
- Development Economics
Upon completion of this course, students should be able to:
1. Describe the characteristics of and the special challenges facing developing nations.
2. Explain alternative theories of economic growth and evaluate their ability to explain the growth experiences of less-developed countries.
3. Discuss the domestic problems that developing nations face, assess the seriousness of these problems, and evaluate the effectiveness of various policies designed to deal with domestic issues.
- Research Methods on Empirical Economics
This course covers the basic econometric concepts and methods used in modern empirical economic research. The goals are to help you understand empirical questions and to develop your skills to conduct empirical analysis. Topics include regression, statistical inference, differences-in-differences, instrumental variables. Depending on time availability, we may introduce some other topics.
- International Political Economics
Along with the changes and evolution in the global politics and economy, the global economic governance has been undergoing various readjustments. The major readjustments are as follows: firstly, the emerging markets are arising as a group and the developed countries are suffering relative decline both in terms of power and governance ability; secondly, the current global economic and financial system is faced with strong pressure to reform itself; thirdly, the emerging and developing countries are obtaining more and more voices and speaking floor and proposing the systematic innovation by means of reform through adding up in global economic governance. These afore-mentioned changes result in the power transfer, shift and dissemination in global political economy. This course is based upon the analyses around the major global economic institutions, such as the WTO, IMF, World Bank, ADB, AIIB, NDB, and etc, focusing upon the processes and driving forces of the current system reforms. After this course, the students are able to master the general background of the global economic governance, in addition to the theories of global economic development and system evolution. The course will analyze the important breaking news in global economic governance, too.
- Topics on Emerging Market Economies
Emerging market economies are the countries which have high economic growth, fast pace of industrialization in Asia, Africa, Latin America, and Eastern Europe. The rise of emerging market economies challenge the existing international economic and political order that has become an important force in the world economy. We plan to give a general introduction of emerging market countries on political, economic and social development, especially focusing on the big developing countries with detailed analysis in the economic field, to enable students to understand general development of these countries, preliminary master the basic law of economic development in emerging market countries, while recognizing its relationship with developed countries and major world powers.
- Social practice
- Master Thesis
Macroeconomics
Textbook:
Mankiw, Gregory, Macroeconomics 9th ed., Worth Publishers
Reference books:
1. Jones, Charles, Macroeconomics, 3rd ed., W. W. Norton & Company
2. Abel, Bernanke and Croushore, Macroeconomics, 9th ed., Pearson
3. Blanchard, Olivier, Macroeconomics, 7th ed., Pearson
4. Romer, David, Advanced Macroeconomics, 4th ed., McGraw Hill Education
Microeconomics
Textbook:
1 .Intermediate microeconomics: a modern approach (9th Edition). Varian, Hal R. NewYork: WW Norton, 2014.
2 .Microeconomics: International Edition, 7/E, Robert Pindyck Daniel Rubinfeld, Pearson Higher Education2009
3. Robert T. Deacon and Jon Sonstelie, “Price Controls and Rent Dissipation with Endogenous Transaction Costs,” American Economic Review, Vol. 81, No. 5 (December 1991) 1361-1373.
4. J. Hirshleifer, “From weakest-link to best-shot: The voluntary provision of public goods”, Public Choice,41 (1983) 371-386.
5. Kelly Bedard, 2001. “Human Capital versus Signaling Models: University Access and High School Dropouts.” Journal of Political Economy, 190(4) (2001) 749-775.
Supplementary (compulsory) materials:
1. Workouts in Intermediate Microeconomics. by Varian, Hal R. and Bergstrom,Theodore C.
2. Microeconomic Analysis, by Varian, Hal R.
International Business and ChinaTextbook:
1. Keith Head, Elements of Multinational Strategy, 2007, Springer (EMS)
2. Feenstra and Wei (eds.), China's Growing Role in World Trade, 2010, The University of Chicago Press (FW)
3. Paul Krugman and Maurice Obstfeld, International Economics, Theory and Policy, 7th ed. (KO)
4. Leamer and Levinsohn, "International Trade Theory: the Evidence", 1995 (LL)
5. Branstetter, Lee and Nicholas Lardy, "China's Embrace of Globalization", 2006, NBER 12373 (BL)
Introduction to Contemporary ChinaReference books:
GUO Peng; CHENG Long; JIANG Xiliang. China Panorama. Higher Education Press. 2012.
Supplementary Student Support Materials:
The required text will be supplemented by outside readings from selected periodicals and journals. Reading of China Daily on a regular basis will be especially helpful in dealing with issues of current interest to this class.
Cross-cultural Exchange and ManagementTextbook:
F. Luthans, and J.P. Doh. International Management: Culture, Strategy, and Behavior, 9th Ed., McGraw-Hill Irwin, 2015. ISBN: 9789814577298
All students are expected to keep abreast of contemporary developments in global business by reading the New York Times, Wall Street Journal, or other major daily, as well as selectively reading various journals such as Forbes, Fortune, Business Week, and other journals.
Chinese
Textbook:
《汉语纵横0:会话课本》
International Finance and ChinaTextbook:
Required: International Monetary and Financial Economics 3rd edition, Thomson
Optional references:
will be given alongside with lectures
International EconomicsTextbooks:
International Trade, Feenstra and Taylor, 2nd edition,
International Economics, Dominick Salvatore, 10th edition, ISBN: 7302244928, 9787302244929
Prerequisites:
Introduction to Microeconomics, Introduction to Macroeconomics, and Calculus I.
Econometrics
Textbook:
Required: A.H. Studenmund. Using Econometrics: A practical Guide (Sixth Editions). Tsinghua University press.
Optional references:
Damodar N. Gujarati and Dawn C. Porter. Essentials of Econometrics. 4th ed. China Machine Press.
Wooldridge, Jeffrey M. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach. 4th ed. South-Western College Pub, 2008.
International MarketingTextbook:
“International Marketing” by Cateora, Gilly, and Graham (16th edition)
China’s Economy
Textbook:
Required: Barry Naughton, 2007, The Chinese Economy, the MIT Press.
Optional references:
1. Lin, Cai and Li, The China Miracle: Development Strategy and Economic Reform,Hong Kong: Chinese University Press .
2. Wu Jinglian, 2005, Understanding and Interpreting Chinese Economic Reform, Singapore: Thomson.
Global Economic Issues and PoliciesTextbook:
1. International Economics, Globalization, and Policy: A Reader,by Philip King and Sharmila King. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 5th edition, 2008.
2. Globalization and Its Discontents, by Joseph Stiglitz. W.W. Norton & Co., 2003
3. The Choice: A Fable of Free Trade and Protection, by Russell Roberts. Prentice Hall, 3rd edition, 2006.
Development EconomicsTextbook:
1. Michael P. Todaro, and Stephen C. Smith. Economic Development, 9th ed. Pearson Addison-Wesley, 2006.
2. N. Gregory Mankiw. Principle of Economics, 4th ed. Cengage Learning Asia Pte. Ltd., 2008
supplementary readings:
1. Gerald M. Meier, James E. Rauch, Leading Issues in Economic Development, Oxford University Press, 2005.
2. Hollis Chenery and T.N. Srinivasan, Handbook of Development Economics, Elsevier Science Pub. Co.,1988-1995.
3. World Bank, World Development Report.
4. World Bank, World Development Indicators.
Research Methods on Empirical EconomicsTextbook:
J. M. Wooldridge, Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach. Thomson South Western, 4th (2008) or 5th Edition.
International Political EconomicsRequired Textbooks
1. Fan Yongming, Modern International Political Economics (second edition), Shanghai People's Publishing House, 2006.
2. Robert Gilpin, The Political Economy of International Relations, Princeton University Press, 1988.
3. Frederic Pearson, International Political Economy, McGraw-Hill Humanities Press, 1999.
Required Readings:
1.Thomas Oatley, International Political Economy: Interests and Institutions in the Global Economy, Longman,2004.
2. Nikilaos Zahariadis, Contending Perspectives in International Political Economy, Peking University Press,2004.
3. Craig N.Murphy, Roger Tooze, The New International Political Economy, Lynne Rienner Publishers.1991.
4. Kurt Burch, Robert A.Denemark, Constituting International Political Economy, Lynne Rienner Publishers.1997.
5. Thormas D.Lairson, David Skidmore, International Political Economy: the Struggle for Power and Wealth, Peking University Press, 2004.
Topics on Emerging Market EconomiesRequired Textbooks:
Paul R. Krugman, Maurice Obstfeld and Marc Melitz, International Economics: Theory and Policy, Addison-Wesley, 9th edition, January 2011